The term "Tibet" here means the whole of Tibet known as Cholka-Sum (U-Tsang, Kham and Amdo). It includes the present-day Chinese administrative areas of the so-called Tibet Autonomous Region, Qinghai Province, two Tibetan Autonomous Prefectures and one Tibetan Autonomous County in Sichuan Province, one Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture and one Tibetan Autonomous County in Gansu Province and one Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Yunnan Province.
Land Size:
2.5 million square kilometres, which includes U-Tsang, Kham and Amdo provinces. “Tibet Autonomous Region”, consisting of U-Tsang and a small portion of Kham, consists of 1.2 million square kilometres. The bulk of Tibet lies outside the “TAR”.
Political Status:
Occupied country and without United Nations’ representation.
Average Altitude:
4,000 metres or 13,000 feet above sea level.
Administration:
Under Chinese rule, Tibet is divided into the following administrative units: a) Tibet Autonomous Region, b) Qinghai Province, c) Tianzu Tibetan Autonomous County and Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Gansu Province, d) Aba Tibetan-Qiang Autonomous Prefecture, Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture and Mili Tibetan Autonomous County in Sichuan Province, e) Dechen Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Yunnan Province.
Population:
The total Tibetan population in Tibet is 6 million. Of them, 2.09 million live in the “TAR” and the rest in the Tibetan areas outside the “TAR”.
Major Rivers:
Yarlung Tsangpo (Brahmaputra in India), Machu (Yellow River in China), Drichu (Yangtse in China), Senge Khabab (Indus in India), Phungchu (Arun in India), Gyalmo Ngulchu (Salween in Burma) and Zachu (Mekong in Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos).
Native Wildlife:
Tibetan antelope, wild yak, wild ass and Tibetan argali, blue sheep, black-necked crane, Tibetan gazelle, giant panda, red panda, golden monkey.
Economy:
Agriculture and animal husbandry.
Literacy Rate:
Approximately 25 per cent.
Brief:
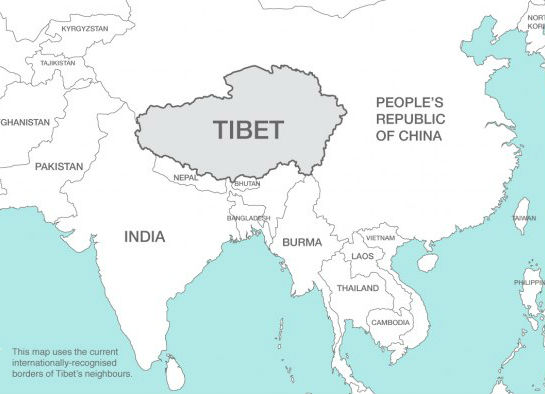
Tibet is located to the south-west of China, also bordering India, Nepal, Burma and Bhutan. Tibet’s three original provinces are U-Tsang, Kham and Amdo. The people in these regions all consider themselves Tibetan, although each has a strong identity and different dialects of Tibetan are used. Under China’s occupation, Tibet has been divided up, renamed and incorporated into Chinese provinces, with little reference to the original borders between Tibet's provinces. When China refers to Tibet, it means the Tibet Autonomous Region or TAR, which includes only U-Tsang and part of Kham. The remainder of Kham was divided between Sichuan and Yunnan Chinese provinces. Amdo was divided between Gansu, Sichuan and Qinghai provinces. The historical territory of Tibet would make it the world's 10th largest nation by geographical area.
Source: Tibetan Government in-Exile


![Tibet has a rich history as a sovereign nation until the 1950s when it was invaded by China. [Photo: File]](/images/stories/Pics-2024/March/Tibet-Nation-1940s.jpg#joomlaImage://local-images/stories/Pics-2024/March/Tibet-Nation-1940s.jpg?width=1489&height=878)